[Top] [Prev] [Next] [Bottom]
This chapter describes how to configure your PortMaster product for routing using the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol. Lucent implements the OSPF protocol as defined in RFC 1583. Also supported are not-so-stubby-areas (NSSAs), defined in RFC 1587, and message-digest 5 (MD5) algorithm authentication, defined in RFC 1321.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
The order of OSPF configuration is very important. Perform the configuration tasks in the following order:
-
Enable the use of OSPF on the PortMaster-see page 3-2.
-
Set the designated and backup router priority-see page 3-2.
-
Set the OSPF areas and ranges-see page 3-2.
-
Enable OSPF on the interfaces-see page 3-3.
-
Enable configuration changes-see page 3-5.
Note ¯  You must enter the save all and reboot commands immediately after enabling or disabling OSPF routing. After you have configured all the desired OSPF settings, enter the save all command to save the configuration changes, and then enter the reset ospf command to restart OSPF routing.
You must enter the save all and reboot commands immediately after enabling or disabling OSPF routing. After you have configured all the desired OSPF settings, enter the save all command to save the configuration changes, and then enter the reset ospf command to restart OSPF routing.
Large OSPF routing tables might require you to upgrade your PortMaster to 4MB or 16MB of memory. See your hardware installation guide for instructions on upgrading PortMaster memory.
You must enable OSPF routing on the PortMaster before you can configure OSPF settings. To enable routing, enter the following commands:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
You must set an OSPF priority for the router. Priorities range from 0 to 255. A calculation is performed on each interface separately to determine the designated router for that interface. The router with the highest priority on a network segment is the designated router. The router with the second highest priority is chosen as the backup designated router that takes over if the designated router becomes unable to perform its duties. If priorities tie, the router with the lower router ID is selected as the designated router. A router assigned priority 0 can never assume the duties of designated router.
To set an OSPF router priority, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf priority Number
In Lucent's current implementation of OSPF, an area is a contiguous set of routers sharing network segments between them. All routers must have at least one interface in area 0.0.0.0, known as the backbone area. Use area 0.0.0.0 if you have only one OSPF area.
To add an OSPF area, enter the following command:
Command> add ospf area Area
You can specify Area in either dotted decimal notation (also known as dotted quad) or decimal notation. For example, the backbone area can be specified as either 0.0.0.0 or 0.
Note ¯  Lucent does not currently support the use of virtual links either to create a noncontiguous area or to enable an area border router to not be directly attached to the backbone.
Lucent does not currently support the use of virtual links either to create a noncontiguous area or to enable an area border router to not be directly attached to the backbone.
You must set one or more ranges of network addresses that define each OSPF area. You can set a maximum of eight ranges for each OSPF area. You can also optionally set the type of OSPF route propagation.
To set an OSPF area range and optional route propagation, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf area Area range Prefix/NM [advertise|quiet|off]
Prefix specifies the destination prefix shared by all IP addresses within the range. NM is the netmask that specifies the number of high-order bits in Prefix that must match addresses to include those addresses within the area. The netmask is a number from 1 to 30, preceded by a slash (/)-for example, /24. Table 1-1 on page 1-7 maps the CIDR representation of netmasks to the hexadecimal notation and to the more familiar dot-separated representation.
Routes to the networks within the range are summarized and propagated to other areas if you use the advertise keyword; this is the default. The routes are not summarized or propagated to other areas if you use the quiet keyword. The off keyword removes the specified range from the area.
Caution ¯  Make sure that the ranges set with this command include the addresses for all PortMaster interfaces within this OSPF area.
Make sure that the ranges set with this command include the addresses for all PortMaster interfaces within this OSPF area.
You can enable or disable the OSPF protocol on an Ethernet interface or on an asynchronous or synchronous network hardwired port.
To set OSPF on the interface, enter the following command-all on one line:
Command> set Ether0 ospf on|off [cost Number] [hello-interval Seconds] [dead-time Seconds]
The on keyword enables OSPF on the specified Ethernet interface. The off keyword disables OSPF on that interface.
You can specify the cost of sending a packet on the interface with a link state metric by using the cost Number keyword and value. The Number metric is a 16-bit decimal number between 1 and 65535. The default is 1.
Routers in OSPF networks continually exchange hello packets with their neighbor routers. You can set the interval that elapses between the transmission of hello packets on the interface by using the hello-interval Seconds keyword and value. Seconds can range from 10 to 120 seconds. The default is 10 seconds.
If the PortMaster stops receiving hello packets from a neighbor, it treats that router as inactive, or down. You can specify how long the PortMaster waits for hello packets from neighbors by using the dead-time Seconds keyword and value. Seconds can range from 40 to 1200 seconds. The default is 40 seconds.
Note ¯  You must set the same cost value, the same hello-interval value, and the same dead-time value on all routers attached to a common network.
You must set the same cost value, the same hello-interval value, and the same dead-time value on all routers attached to a common network.
To set OSPF on an asynchronous or synchronous port, enter the following command-all on one line:
Command> set S0|W0 ospf on|off [cost Number] [hello-interval Seconds] [dead-time Seconds] [nbma|point-to-multipoint|wan-as-stub-ptmp]
The on keyword enables OSPF on the specified asynchronous (S0) or synchronous (W0) port. The off keyword disables OSPF on that port.
After you make all the desired configuration changes, enter the following commands:
Command> save all
Command> reset ospf
The save all command writes all configuration changes to the nonvolatile memory of the PortMaster. The reset ospf command performs the following steps to recreate OSPF startup conditions:
This section describes additional commands that you might need for your OSPF configuration.
You can specify an area password or key to use when you communicate to other routers in the area. The password must be an ASCII string of from 1 to 8 characters.
To set the password, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf area Area password String
You can specify an MD5 secret for an OSPF area. All routers in the area must have the same key number associated with the MD5 secret.
Caution ¯  Overwriting the current key number with the same number causes the secret to be lost immediately-that is, without rebooting.
Overwriting the current key number with the same number causes the secret to be lost immediately-that is, without rebooting.
To set the key number and the secret for MD5 authentication, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf area Area md5 Number String
The key ID Number associated with the MD5 secret must be an integer between 1 and 255. The MD5 secret String must be an ASCII string of between 1 and 16 characters.
When an MD5 key number and secret are changed, both the old and new numbers and secrets remain valid until either the reboot or reset ospf command is entered.
Note ¯ The Ether0 IP address is used by default if you set the OSPF router address to 0.0.0.0 or the ID number to 0.  Lucent strongly recommends that you use the default setting.
Lucent strongly recommends that you use the default setting.
To set the OSPF router IP address or ID number, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf router-id Ipaddress|Number
Caution ¯  Be careful when using this feature. When you set a new router ID, the links belonging to an old router ID take as long as 1 hour to expire. Routing instability can result during the expiration period.
Be careful when using this feature. When you set a new router ID, the links belonging to an old router ID take as long as 1 hour to expire. Routing instability can result during the expiration period.
The propagation settings enable you to specify how routes coming from one routing protocol are translated and advertised by the PortMaster into another routing protocol.
Because external routes can be propagated into transit areas, but not into stub areas, you can determine external route propagation into OSPF areas by defining an area as either a transit area or a stub area.
The backbone area is always defined as a transit area.
A stub area does not attach to any area except the backbone and has no exit other than to the backbone. Because external routes are not propagated to stub areas, stub areas must be given a default route to reach external destinations. See "Injecting the Default Route into a Stub Area or NSSA" on page 3-11 for more information.
To set the propagation of external routes by defining an area as either a transit area or a stub area, use the following command. The keyword on defines the area as a transit area. The keyword off defines the area as a stub area.
Command> set ospf area Area external on|off
For routers running both OSPF and RIP on a network, you can enable the propagation of RIP routes learned on a specified Ethernet interface from other routers into OSPF as OSPF Type 2 external routes. See Table 1-6 on page 1-17 for a description of OSPF route types.
To set RIP route propagation, enter the following command:
Command> set Ether0 ospf accept-rip on|off
If the RIP routes learned on the Ethernet interface originate from routers that are always running both OSPF and RIP, you can avoid duplicating route information by using the default off setting for RIP-to-OSPF propagation.
The propagation filter is an IP access filter that you create in the filter table on the PortMaster. It uses the source addresses specified in the filter list to indicate routes.
Refer to the instructions for configuring filters in the Configuration Guide for PortMaster Products for information on setting filters.
To define a propagation filter, enter the following commands:
Command> add filter Filtername
Command> set filter Filtername RuleNumber permit|deny Prefix(src)/NM Prefix(dest)/NM
Add other keywords and values as needed to the set filter command.
You define a propagation rule to determine how routes coming into the PortMaster in one protocol are translated and advertised in another protocol. You insert the rule into a filter after you create the filter. The filter is stored in the filter table of the PortMaster.
To define a propagation rule, enter the following command-all on one line:
Command> add propagation Protocol(src) Protocol(dest) Metric Filtername
Command> reset propagation
Use the appropriate keyword-rip, static, ospf, bgp-to designate the source and destination protocols. Metric is a common metric used to translate from one protocol to another. A 0 metric causes the PortMaster to attempt to build a metric automatically.
Caution ¯  If you plan to use a constant metric instead of the automatically generated metric provided by the ComOS, you run the risk of creating routing loops if you do not provide for filters or policies to screen the route information the PortMaster accepts from each routing protocol.
If you plan to use a constant metric instead of the automatically generated metric provided by the ComOS, you run the risk of creating routing loops if you do not provide for filters or policies to screen the route information the PortMaster accepts from each routing protocol.
Follow this procedure to change or delete a propagation rule:
-
Delete the existing propagation rule as follows:
Command> delete propagation Protocol(SRC) Protocol(dest)
-
If you are changing a rule, add the revised propagation rule as follows:
Command> add propagation Protocol(SRC) Protocol(dest) Metric Filtername
-
Reset the propagation rules system as follows:
Command> reset propagation
-
Follow any additional instructions prompted by the PortMaster.
Apply a propagation route filter to a specific interface by entering the following command:
Command> set Ether0|S0|W1 route-filter in|out Filtername
Command> reset ospf
The route filter is a packet filter that you create in the filter table on the PortMaster. You must specify the Ethernet, asynchronous, or synchronous interface to which the filter is applied. You must also specify whether the filter is applied for inbound or outbound traffic.
Refer to instructions for configuring filters in the Configuration Guide for PortMaster Products for information about setting filters.
The effects of route filters depend on the protocol being filtered and on whether the filter is for inbound or outbound routes.
Table 3-1 describes the effects of route filters.
Not-so-stubby areas (NSSAs) are similar to stub areas except that a form of Type 1 and Type 2 external routes can be learned from NSSAs. The N1/N2 routes learned from an NSSA are translated into corresponding external routes for the backbone and other transit areas that accept external routes. As for stub areas, default costs can be set for NSSAs. See "Setting a Stub Area or NSSA Default Route" on page 3-59 for more information. External routes are not advertised into NSSAs.
To define an area as an NSSA, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf area Area nssa on|off
You can specify the cost of sending a packet on the interface with a link state metric by using the cost Number keyword and value. The Number metric is a 16-bit decimal number between 1 and 65535. The default is 1.
Routers in OSPF networks continually exchange hello packets with their neighbor routers. You can set the interval that elapses between the transmission of hello packets on the interface by using the hello-interval Seconds keyword and value. Seconds can range from 10 to 120 seconds. The default is 10 seconds.
If the PortMaster stops receiving hello packets from a neighbor, it treats that router as inactive, or down. You can specify how long the PortMaster waits for hello packets from neighbors by using the dead-time Seconds keyword and value. Seconds can range from 40 to 1200 seconds. The default is 40 seconds.
You can specify how OSPF is handled based on the kind of Frame Relay network being used.
-
Configure a point-to-multipoint interface when the show ospf link command
displays a large number of available routes, but the show routes command
displays no routes learned over the Frame Relay interface.
-
Use the show ospf links command to check the router LSAs of your neighbors on
the Frame Relay network. If they show stub network link entries for the Frame
Relay network with the netmask for that network, configure the interface as
wan-as-stub-ptmp. If they show the Frame Relay network as a host route with a
mask of 255.255.255.255, then configure the interface as point-to-multipoint.
You can enable an area border router to create and inject the default route (0.0.0.0) into a stub area or NSSA. The default route is advertised to a stub area or NSSA when you specify a cost-an integer from 0 to 15. Lower costs are preferred.
To enable the injection of external routes into a stub area or NSSA, enter the following command:
Command> set ospf area Area stub-default-cost Cost
To disable the injection of external routes into a stub area, specify a cost of 0.
Several commands enable you to display detailed information about your OSPF configuration.
To display information on the configured OSPF areas, enter the following command:
Command> show ospf areas
To display a summary of the OSPF database with one line per link state advertisement (LSA), enter the following command-all on one line:
Command> show ospf links [router|network|summary|external|nssa]
To show information about routers directly accessible through your network interfaces, enter the following command:
Command> show ospf neighbor
See the Command Line Administrator's Guide for detailed explanations and examples of these commands.
This section provides the following examples of OSPF network configurations:
This example shows how to connect two OSPF areas over a single WAN connection using numbered serial ports. The example uses PortMaster Office Routers on Ethernet (see Figure 3-1), although any PortMaster router or network type could be used.
Note ¯  Because OSPF applies an area to each port that falls within the range you set for it, any port or network segment over which you want to propagate OSPF must be in the same range.
Because OSPF applies an area to each port that falls within the range you set for it, any port or network segment over which you want to propagate OSPF must be in the same range.
For a discussion of typical problems encountered in this type of configuration, see "Propagating OSPF over a WAN Link" on page A-15 in Appendix A.
Figure 3-1 Propagating OSPF over a WAN Link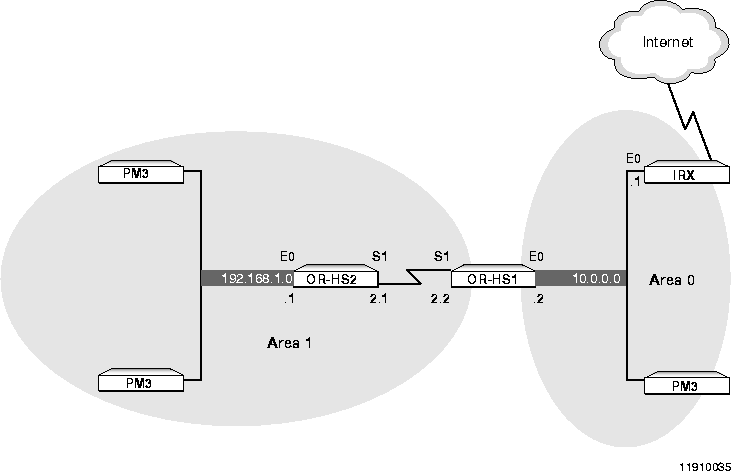
The order of OSPF configuration is important. First set priority (and router ID if desired), then set areas and ranges, and finally enable OSPF for the interfaces.
The complete configuration for OR-HS2 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring OS-HS2:
-
Set the local IP address of the network hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set S1 address 192.168.2.1
Port S1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.2.1
-
Set the IP address of the remote router for a network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set S1 destination 192.168.2.2
Port W1 destination changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.2.2
-
Enable the use of OSPF on this router:
Command> set ospf enable
OSPF will be enabled after next reboot
-
Save the configuration and reboot the router:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
Command> reboot
-
Add Area 1 to the area tables of OR-HS2:
Command> add ospf area 1
New Area successfully added
-
Set the ranges of network addresses that define the OSPF area:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 192.168.2.0/24
Area successfully updated
-
Set the Area 1 OSPF range for the Ethernet port:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 192.168.1.0/24
Area successfully updated
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the synchronous network hardwired port:
Command> set S1 ospf on
S1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the Ethernet interface:
Command> set Ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Reset the synchronous network hardwired port:
Command> reset S1
Resetting port S1
-
Save the configuration:
Command> save all
Command> reset ospf
The complete configuration for OR-HS1 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring OS-HS1:
-
Set the local IP address of the network hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set S1 address 192.168.2.2
Port S1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.2.2
-
Set the IP address of the remote router for a network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set S1 destination 192.168.2.1
Port W1 destination changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.2.1
-
Enable the use of OSPF on this router:
Command> set ospf enable
OSPF will be enabled after next reboot
-
Save the configuration and reboot the router:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
Command> reboot
-
Add Area 0 to the area tables of OR-HS1:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the ranges of network addresses that define OSPF Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 10.0.0.0/8
Area successfully updated
-
Add Area 1 to the area tables of OR-HS1:
Command> add ospf area 1
New Area successfully added
-
Set the ranges of network addresses that define OSPF Area 1:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 192.168.2.0/24
Area successfully updated
-
Set the Area 1 OSPF range for the Ethernet port:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 192.168.1.0/24
Area successfully updated
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the synchronous network hardwired port:
Command> set S1 ospf on
S1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the Ethernet interface:
Command> set Ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Reset the synchronous network hardwired port:
Command> reset S1
Resetting port S1
-
Save the configuration:
Command> save all
Command> reset ospf
The most basic OSPF scenario in a nonbroadcast multiaccess (NBMA) network is a single network in a single OSPF area. Figure 3-2 shows a more typical scenario, which includes more than one network in a single area. In this configuration, all routers that are members of the network can respond to any ARP packet that goes out on the network.
Although this example uses Ethernet, the example applies as well to any network type.
Note ¯  Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
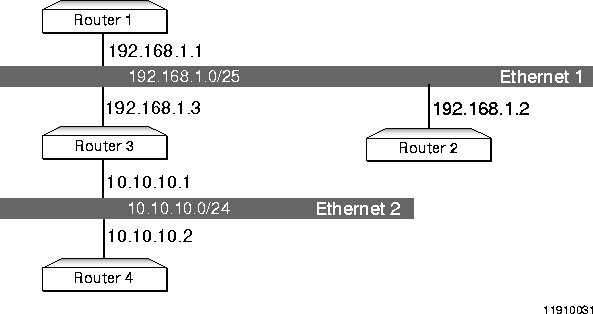 NBMA
NBMA
Assumptions:
The complete configuration for Router 1 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 1:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.1
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.1
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 2
OSPF priority changed from 0 to 2
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Ethernet 1:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set the OSPF area range for Ethernet 2:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 2 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 2:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 192.168.1.1
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.1, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.2
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.2
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 255.255.255.128 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set the OSPF area range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 3 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 3:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 192.168.1.1
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.1, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet 0 address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.3
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.3
-
Set the Ethernet 0 netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the Ethernet 1 address:
Command> set ether1 address 10.10.10.1
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 10.10.10.1
-
Set the Ethernet 1 netmask:
Command> set ether1 netmask 255.255.255.0
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.0
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 1
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 1
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set the OSPF area range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 4 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 4:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 10.10.10.1
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 10.10.10.1, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet 0 address:
Command> set ether0 address 10.10.10.2
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 10.10.10.2
-
Set the Ethernet 0 netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.0
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.0
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set the OSPF area range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
Figure 3-3 shows a slightly more complex OSPF network configuration than that shown in Figure 3-2, involving multiple areas.
Note ¯  Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
NBMA Multiple Areas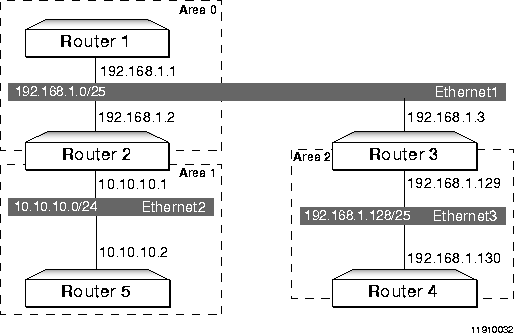
Assumptions:
The complete configuration for Router 1 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 1:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
-
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.1
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.1
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 2
OSPF priority changed from 4 to 2
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Ethernet 1:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 2 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 2:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 192.168.1.1
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.1, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet 0 address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.2
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.2
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the Ethernet 1 address:
Command> set ether1 address 10.10.10.1
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 10.10.10.1
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether1 netmask 255.255.255.0
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 2 to 0
-
Define the OSPF Area 0:
Command> add ospf Area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF Area 0 range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Define the OSPF Area 1:
Command> add ospf area 1
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF Area 1 range:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet 0 OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set Ethernet 1 OSPF on:
Command> set ether1 ospf on
Ether1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 3 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 3:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 192.168.1.1
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.1, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet 0 address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.3
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.3
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the Ethernet 1 address:
Command> set ether1 address 192.168.1.129
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.129
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 1
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 1
-
Define the OSPF Area 0:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF Area 0 range:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/25
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Define the OSPF Area 2:
Command> add ospf area 2
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF Area 2 range:
Command> set ospf area 2 range 192.168.1.128/15
Range 192.168.1.128 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet 0 OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set Ethernet 1 OSPF on:
Command> set ether1 ospf on
Ether1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 4 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 4:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 192.168.1.129
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.129, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet 0 address:
Command> set ether0 address 192.168.1.130
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.130
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.128
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 0
-
Define the OSPF Area 1:
Command> add ospf area 1
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF Area 1 range:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet 0 OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 5 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 5:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the gateway router:
Command> set gateway 10.10.10.1
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to 10.10.10.1, metric = 1
-
Set the Ethernet 0 address:
Command> set ether0 address 10.10.10.2
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 10.10.10.2
-
Set the Ethernet netmask:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.0
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.0
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 1
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 1
-
Define the OSPF Area 1:
Command> add ospf area 1
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF Area 1 range:
Command> set ospf area 1 range 10.10.10.0/24
Range 10.10.10.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set Ethernet 0 OSPF on:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The fully meshed Frame Relay network in Figure 3-4 is another example of a nonbroadcast multiaccess configuration. The significant difference between this configuration and the configuration in Figure 3-2 is that the network medium type in Figure 3-4 is Frame Relay.
Note ¯  Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
NBMA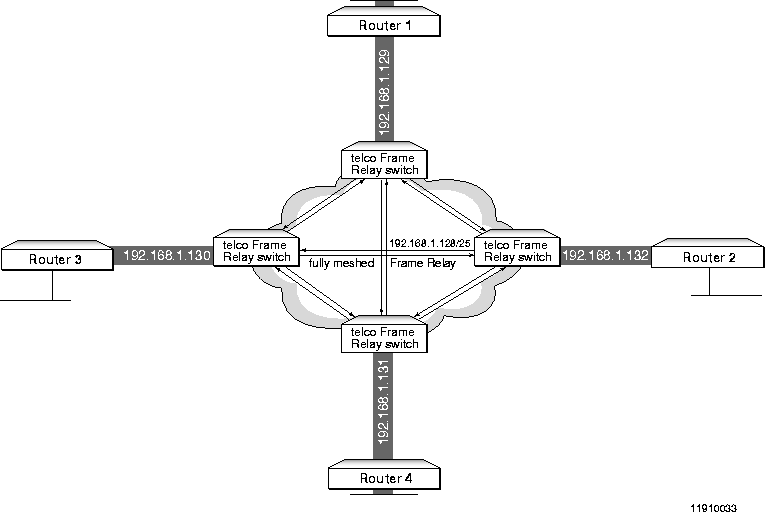 Fully Meshed Frame Relay
Fully Meshed Frame Relay
The complete configuration for Router 1 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 1:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 1
OSPF priority changed from 3 to 1
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.129
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.129
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 ospf on
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 2 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 2:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 2
OSPF priority changed from 4 to 2
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.132
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.132
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 ospf on
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 3 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 3:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 3 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.131
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.131
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 ospf on
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 4 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 4:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 4 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.130
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.130
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 ospf on
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
Because permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) are provided by the access carrier and can be expensive, a fully meshed configuration might not be cost-effective. Also, if your organization has multiple remote sites with virtual circuits built into concentration routers at the central site, a hub and spoke configuration might be a better solution.
In Figure 3-5, although Router 4 is not directly linked to Route 3 and Router 5, it can communicate with them (is partially meshed) via its PVC connection with Router 2.
Note ¯  Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
Because this example is not concerned with configuring the gateway, no gateway address or netmask is included in the illustration or example configuration.
Point-to-Multipoint Partially Meshed Frame Relay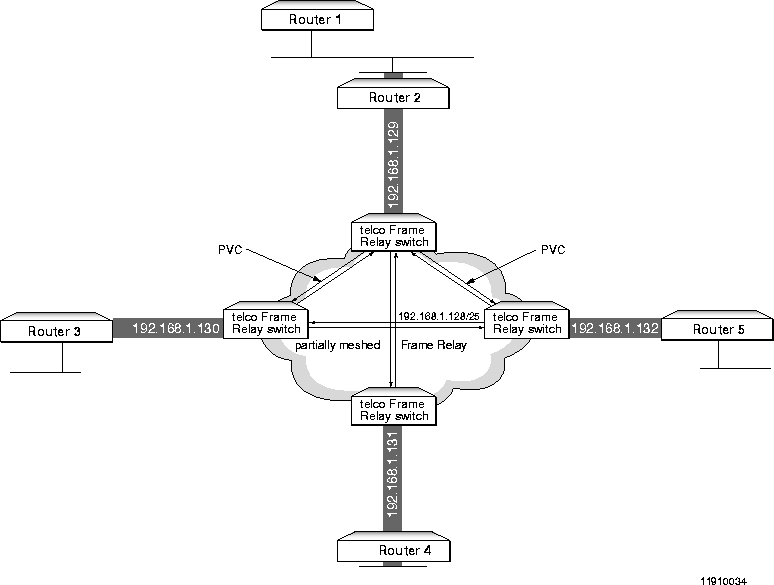
The complete configuration for Router 2 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 2:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 1
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 1
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.129
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.129
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port and set it as the interface to a point-to-multipoint Frame Relay network:
Command> set w1 ospf on point-to-multipoint
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 3 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 3:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.130
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.130
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port and set it as the interface to a point-to-multipoint Frame Relay network:
Command> set w1 ospf on point-to-multipoint
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 4 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 4:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.131
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.131
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port and set it as the interface to a point-to-multipoint Frame Relay network:
Command> set w1 ospf on point-to-multipoint
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
The complete configuration for Router 5 appears in the following box:
The following procedure shows the separate tasks for configuring Router 5:
-
Enable OSPF on the router:
Command> set ospf enable
Command> save all
Command> reboot
-
Set the IP address of the upstream gateway router:
Command> set gateway x.x.x.x
Gateway changed from 0.0.0.0 to x.x.x.x, metric = 1
-
Set the address of the Ethernet interface:
Command> set ether0 address y.y.y.y
Local (ether0) address changed from 0.0.0.0 to y.y.y.y
-
Set the netmask of the Ethernet subnet:
Command> set ether0 netmask 255.255.255.z
Ether0 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.z
-
Set the router priority:
Command> set ospf priority 0
OSPF priority changed from 5 to 0
-
Define the OSPF area:
Command> add ospf area 0
New Area successfully added
-
Set the OSPF area range for Area 0:
Command> set ospf area 0 range 192.168.1.0/24
Range 192.168.1.0 for area 0.0.0.0 successfully updated
Area successfully updated
-
Set OSPF on for ether0:
Command> set ether0 ospf on
Ether0 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Set the network type for the synchronous port:
Command> set w1 network hardwired
Port type for port W1 changed from Network to Network(hardwired)
-
Set the transport protocol for the hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 protocol frame
Port type for port W1 changed from ppp to frame relay
-
Set the local management interface polling interval:
Command> set w1 lmi 10
LMI keepalive timer for W1 changed from 0 to 10
-
Set the local IP address for the hardwired synchronous port to create a numbered interface:
Command> set w1 address 192.168.1.132
Port W1 local address changed from 0.0.0.0 to 192.168.1.132
-
Set the IP netmask of the remote router for the network hardwired synchronous port:
Command> set w1 netmask 255.255.255.128
W1 netmask changed from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.128
-
Enable the OSPF protocol on the hardwired synchronous port and set it as the interface to a point-to-multipoint Frame Relay network:
Command> set w1 ospf on point-to-multipoint
W1 ospf state changed from off to on
-
Save changes:
Command> save all
Saving global configuration
Saving ports
User table successfully saved
Hosts table successfully saved
Static route table successfully saved
Location table successfully saved
SNMP table successfully saved
Filter table successfully saved
New configurations successfully saved
-
Make OSPF configuration effective:
Command> reset ospf
Resetting OSPF
[Top] [Prev] [Next] [Bottom]
spider@livingston.com
Copyright © 1998, Lucent Technologies. All rights
reserved.
 Lucent strongly recommends that you use the default setting.
Lucent strongly recommends that you use the default setting.


